Rheumatoid arthritis is a destructive autoimmune disease driven by the effects of pathogenic autoantibodies and pro-inflammatory cytokines. It causes chronic pain, stiffness and swelling of joints. There are several genetic, non-genetic and environmental factors believed to contribute to the onset of rheumatoid arthritis. We’ve been learning more and more about each of those factors in recent years.
People with rheumatoid arthritis produce antibodies that react with antigens made by their own bodies; these are called autoantibodies.
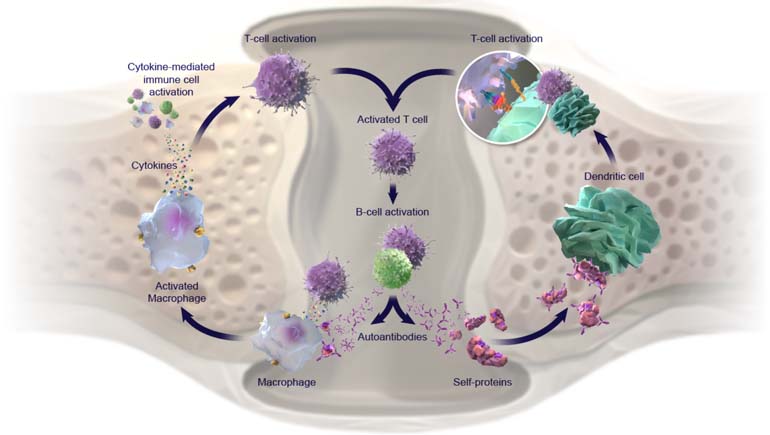
Unlike in a healthy person where the initiation of the immune system is in response to infection and disease, in rheumatoid arthritis, immune cells, called T cells, influence the activation of another type of immune cell, called B cells, to produce antibodies. These autoantibodies play important roles in the development of rheumatoid arthritis. In rheumatoid arthritis, autoantibodies along with other drivers, mediate inflammation and cytokine release. The release of T cell–derived cytokines can lead to macrophage activation. Macrophage activation in the rheumatoid joint leads to further secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines, including IL-1, IL-6, IL-8, and TNF-α, which all coordinate to drive further T-cell activation.
The role of pro-inflammatory cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis is well known, and recent research has deepened our understanding of the role of pathogenic autoantibodies in disease. Two autoantibodies common in rheumatoid arthritis are rheumatoid factor (RF) and anti-citrullinated protein antibodies (ACPA), both of which have been well studied. They are found in 60-80% and 70-90% of rheumatoid arthritis cases, respectively.
While RF has been an established severity factor in rheumatoid arthritis, new findings have shed a light on the role of ACPA in driving disease progression. Since we are still learning about the role of ACPA in rheumatoid arthritis, it is important for physicians to be aware of this ongoing research.
Why is knowing if a patient is positive for autoantibodies important?